Firewall Deployment
Firewall installtion in Kolkata
What Is Firewall?
Firewall is a network security device that observes and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic, adhering to the security policies defined by an organization. Essentially, it acts as a protective wall between a private internal network and the public Internet.
Fencing your property protects your house and keeps trespassers at bay; similarly, firewalls are used to secure a computer network. Firewalls are network security systems that prevent unauthorized access to a network. It can be a hardware or software unit that filters the incoming and outgoing traffic within a private network, according to a set of rules to spot and prevent cyberattacks.
Firewalls are used in enterprise and personal settings. They are a vital component of network security. Most operating systems have a basic built-in firewall. However, using a third-party firewall application provides better protection.
Now that we have understood what is firewall, moving forward we will see the history of firewalls.
Types of Firewalls
A firewall can either be software or hardware. Software firewalls are programs installed on each computer, and they regulate network traffic through applications and port numbers. Meanwhile, hardware firewalls are the equipment established between the gateway and your network. Additionally, you call a firewall delivered by a cloud solution as a cloud firewall.
There are multiple types of firewalls based on their traffic filtering methods, structure, and functionality. A few of the types of firewalls are:
Packet Filtering
A packet filtering firewall controls data flow to and from a network. It allows or blocks the data transfer based on the packet’s source address, the destination address of the packet, the application protocols to transfer the data, and so on.
Proxy Service Firewall
This type of firewall protects the network by filtering messages at the application layer. For a specific application, a proxy firewall serves as the gateway from one network to another.
Stateful Inspection
Such a firewall permits or blocks network traffic based on state, port, and protocol. Here, it decides filtering based on administrator-defined rules and context.
Next-Generation Firewall
According to Gartner, Inc.’s definition, the next-generation firewall is a deep-packet inspection firewall that adds application-level inspection, intrusion prevention, and information from outside the firewall to go beyond port/protocol inspection and blocking.
Unified Threat Management (UTM) Firewall
A UTM device generally integrates the capabilities of a stateful inspection firewall, intrusion prevention, and antivirus in a loosely linked manner. It may include additional services and, in many cases, cloud management. UTMs are designed to be simple and easy to use.
Threat-Focused NGFW
These firewalls provide advanced threat detection and mitigation. With network and endpoint event correlation, they may detect evasive or suspicious behavior.
How Does a Firewall Work?
As mentioned previously, firewalls filter the network traffic within a private network. It analyses which traffic should be allowed or restricted based on a set of rules. Think of the firewall like a gatekeeper at your computer’s entry point which only allows trusted sources, or IP addresses, to enter your network.
A firewall welcomes only those incoming traffic that has been configured to accept. It distinguishes between good and malicious traffic and either allows or blocks specific data packets on pre-established security rules.
These rules are based on several aspects indicated by the packet data, like their source, destination, content, and so on. They block traffic coming from suspicious sources to prevent cyberattacks.
For example, the image depicted below shows how a firewall allows good traffic to pass to the user’s private network.

However, in the example below, the firewall blocks malicious traffic from entering the private network, thereby protecting the user’s network from being susceptible to a cyberattack.


This way, a firewall carries out quick assessments to detect malware and other suspicious activities.There are different types of firewalls to read data packets at different network levels. Now, you will move on to the next section of this tutorial and understand the different types of firewalls.
Why Are Firewalls Important?
Firewalls are designed with modern security techniques that are used in a wide range of applications. In the early days of the internet, networks needed to be built with new security techniques, especially in the client-server model, a central architecture of modern computing. That’s where firewalls have started to build the security for networks with varying complexities. Firewalls are known to inspect traffic and mitigate threats to the devices.
Advantages of Using Firewalls
Now that you have understood the types of firewalls, let us look at the advantages of using firewalls.
- Firewalls play an important role in the companies for security management. Below are some of the important advantages of using firewalls.
- It provides enhanced security and privacy from vulnerable services. It prevents unauthorized users from accessing a private network that is connected to the internet.
- Firewalls provide faster response time and can handle more traffic loads.
- A firewall allows you to easily handle and update the security protocols from a single authorized device.
- It safeguards your network from phishing attacks.
- Cybersecurity
- Types of Cyber Attacks
- IT vs OT Cybersecurity
- AI Cybersecurity
- Cyber Threat Intelligence
- Cybersecurity Management
- Network Security
- Data Security
- Email Security
- Endpoint Security
- Web Security
- Enterprise Security
- Cybersecurity Mesh
Firewall Description in Shorts
A firewall is a security system—software, hardware, or both—that monitors and controls network traffic based on predefined rules. Its main job is to block unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication between devices and networks.
Our Top Firewall Services
















High End Core Data Center Firewall
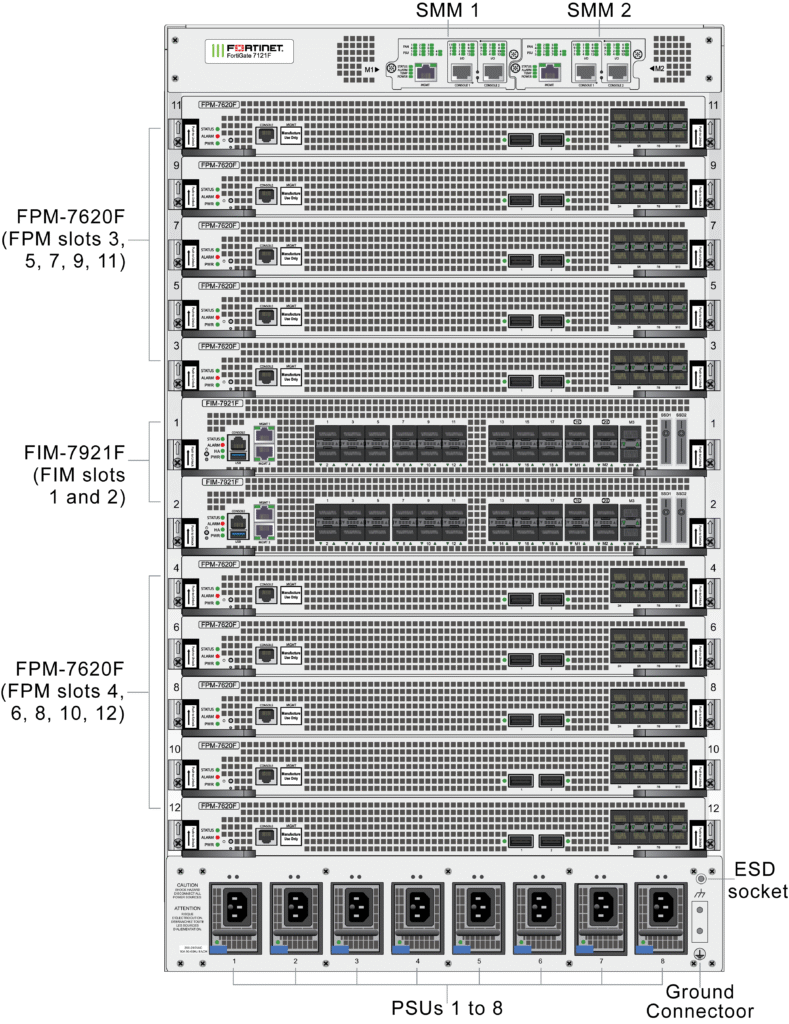
FortiGate-7121F 16U 12-slot chassis with 2x FPM-7620F Processor Module, 2x FIM-7921F I/O Module , 2x Management Module and 8x hot swappable redundant PSU


High Performance with Flexibility The FortiGate 7000F Series delivers high performance security-driven networks to large enterprises and service providers that can weave security deep into their datacenter and across their hybrid IT architecture to protect any edge at any scale.
Firewall Protection Supported:
- Malware Protection
- Antivirus
- Anti-spam
- URL Filtering
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
- Zero Day Event
- Ransomware Protection
- Threat Protection
- Content Filtering
- Outbreak Prevention
- TLS Decryption
- Data Loss Prevention
- SaaS Security
- DNS Security
- Application Control
Firewall Throughput: 1890 Gbit/s
Encryption Standard:
- SSL
- TLS 1.3
- AES (256-bit) SHA-256
- Number of VPN Supported: 30000
- Connectivity Technology: Wired
- Number of Concurrent Sessions (Max): 1e+09
- AI-powered: Yes
AI Features:
- Anti-malware
- Enterprise Security
- USB: Yes
- VPN Throughput: 78.75 GB/s
- IPS Throughput: 84.38 GB/s
- Total Number of Expansion Slots: 12
Expansion Slot Type:
- Processor Module
- I/O Module
- Management Module
- Manageable: Yes
- Power Consumption: 9754 W
- Compatible Rack Unit: 16U
- Form Factor: Rack-mountable
- Height: 28.6″
- Width: 17.3″
- Depth: 26.6″
- Weight (Approximate): 447.36 lb
Package Contents:
- FortiGate FG-7121F-DC Firewall Chassis
- 4 x 10 GE SFP+ SR Transceivers Module
- 2 x FPM-7620F Processor Module
- 2 x FIM-7921F I/O Module
- 2 x Management Module
- 8 x Hot Swappable Redundant PSU 2KW DC-DC
FortiOS Everywhere | FortiOS, Fortinet’s Advanced Operating System
FortiOS enables the convergence of high performing networking and security across the Fortinet Security Fabric. Because it can be deployed anywhere, it delivers consistent and context-aware security posture across network, endpoint, and multi-cloud environments. Data Sheet
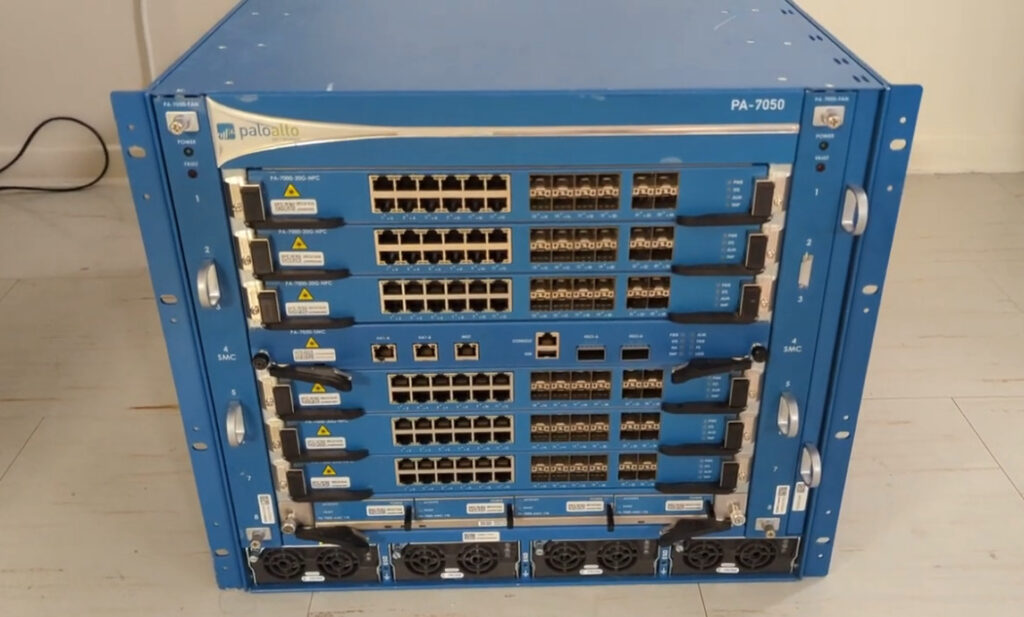
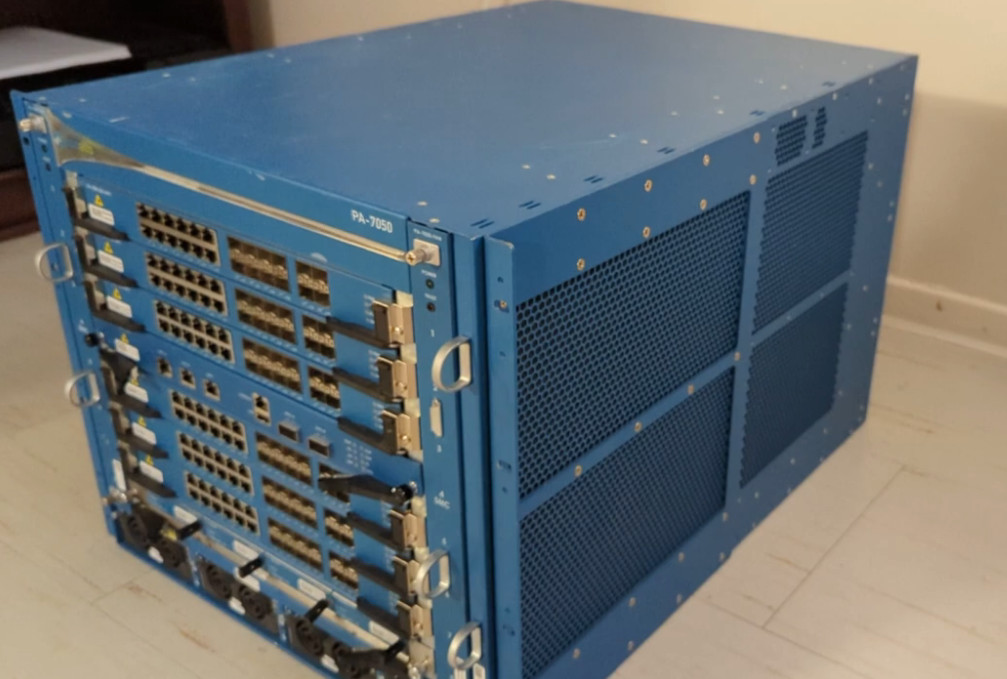


PA-7000 Series High Performance Firewall
Palo Alto Networks PA-7000 Series ML-Powered Next Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) enable enterprise-scale organizations and service providers to deploy security in high-performance environments, such as large data centers and high-bandwidth network perimeters. Designed to handle growing throughput needs for pplication-, user-, and device-generated data, these systems offer amazing performance, prevention capabilities to stop the most advanced cyberattacks, and high-throughput decryption to stop threats hiding under the veil of encryption. Built to maximize security processing resource utilization and automatically scale as new computing power becomes available, the PA-7000 Series offers simplicity defined by a single system approach to management and licensing Data Sheet
Contact Now
For more information about Networking or to install a Router, Switch, Firewall,etc in your company, contact us now by calling or emailing us by pressing the button below. We are ready to help you.
